A recent study conducted by a research group at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has shed light on the formation and behavior of excitons in van der Waals magnets. These microscopic, particle-like objects play a crucial role in understanding the optical and magnetic properties of materials like nickel phosphorus trisulfide (NiPS3).
Excitons: An Overview
Excitons are composed of an electron and a positively charged “hole” within a crystal. The discovery of excitons in NiPS3 has generated considerable interest due to the potential correlation between excitons and magnetism. This connection could pave the way for revolutionary technologies based on magnetism, such as advanced information storage solutions.
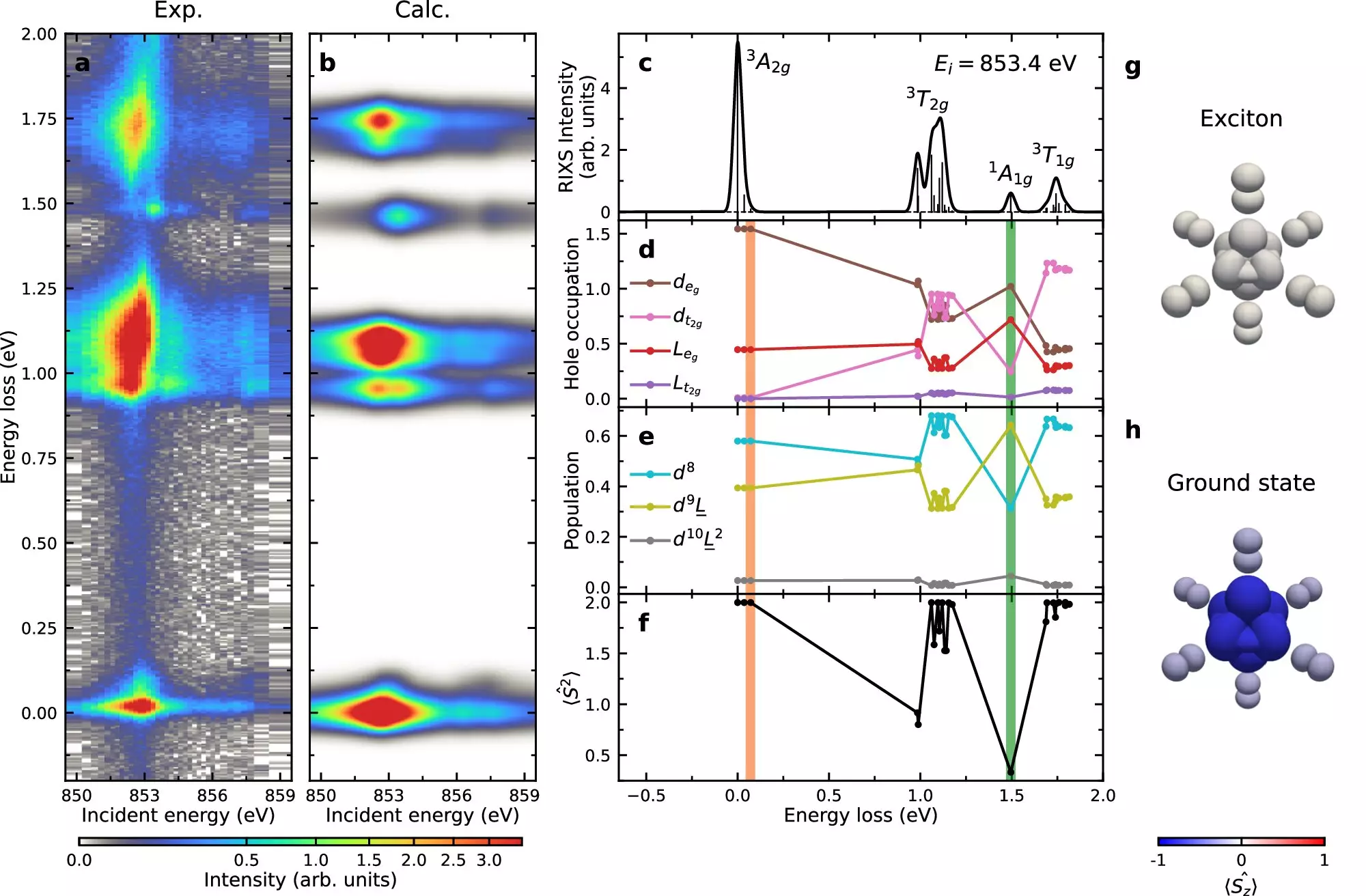
Researchers utilized the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II) at Brookhaven to investigate the behavior of excitons in NiPS3. By employing resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at the Soft Inelastic X-ray Scattering (SIX) beamline, scientists were able to obtain high-resolution insights into the electronic properties of the material.
The study revealed that exciton formation and propagation in NiPS3 are governed by the Hund’s exchange interaction, a fundamental physics principle. This interaction determines the energy required for exciton formation by influencing different electron spin configurations. Additionally, the researchers observed that excitons disperse through the crystal in a manner resembling a “double-magnon” spin disturbance, highlighting the intricate relationship between excitons and magnons in van der Waals magnets.
As advanced techniques like RIXS and electron microscopy continue to evolve, scientists anticipate making further advancements in understanding materials like NiPS3. These cutting-edge instruments offer the potential for enhanced measurements and insights into the behavior of excitons and their interaction with magnetism.
The study conducted by the research group at Brookhaven National Laboratory underscores the intricate interplay between excitons and magnetism in van der Waals magnets. By unraveling the formation and behavior of excitons in materials like NiPS3, scientists are paving the way for future innovations in the realm of magnetism-based technologies. The findings from this research not only enhance our understanding of these complex materials but also open up new avenues for exploring the potential applications of excitons in various technological fields.

Leave a Reply